Divisibility rules-
Divisibility by 2, 5 and 10
A number is divisible by 2 if the final digit (the digit in the ones place) is even. Numbers ending in 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8 therefore are divisible by 2. A number is divisible by 5 if the final digit is a 0 or a 5. A number is divisible by 10 if the final digit is a 0.
Divisibility by 3, 6 and 9
A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. For example, 285 is divisible by 3 because 2 + 8 + 5 = 15 is divisible by 3. A number is divisible by 6 if it is divisible by both 3 and 2 (see above rules). A number is divisible by 9 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 9. For examples, 285 is not divisible by 9 because 2 + 8 + 5 = 15 is not divisible by 9.
Divisibility by 4, 7 and 8
A number is divisible by 4 if the last two digits of the number are divisible by 4. For 7, there are a couple of strategies to use.
A number is divisible by 8 if the last three digits are divisible by 8. This is the standard rule which can be a little sketchy for larger numbers, like who knows if 680 is divisible by 8? Because of this, we offer our Math-Drills.com solution which requires a little arithmetic, but can be accomplished quite easily with a little practice. As you know 8 is 2 to the third power, so we thought if you could divide the last three digits of a number by 2 three times, it would be divisible by 8. 680 ÷ 2 ÷ 2 ÷ 2 = 340 ÷ 2 ÷ 2 = 170 ÷ 2 = 85. We have a winner! 680 is indeed divisible by 8.
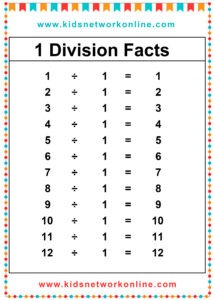
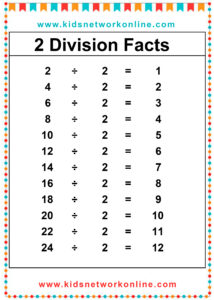
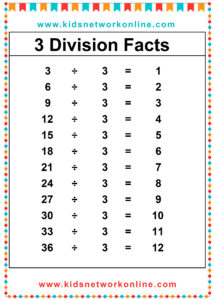
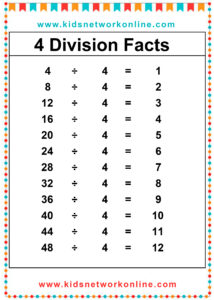
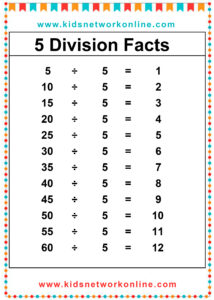
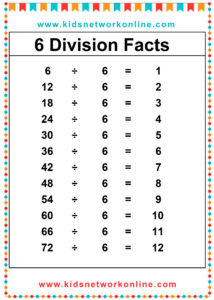
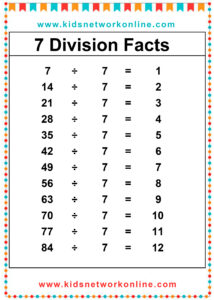
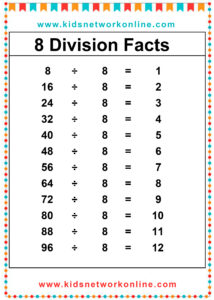
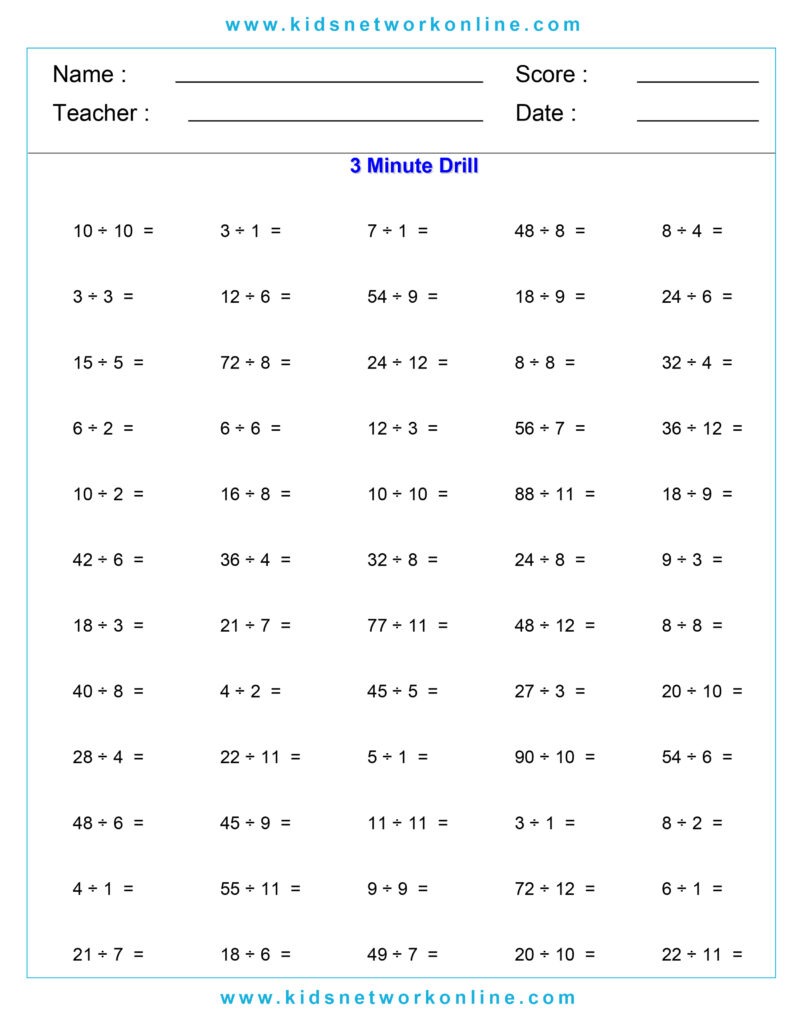
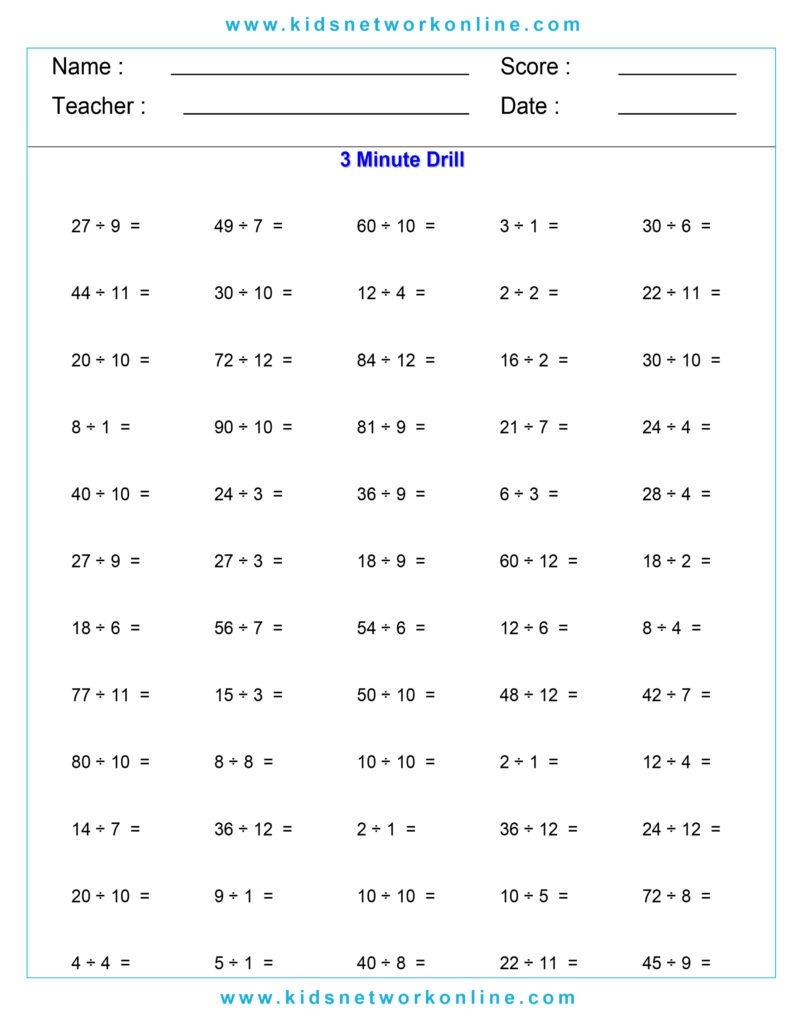
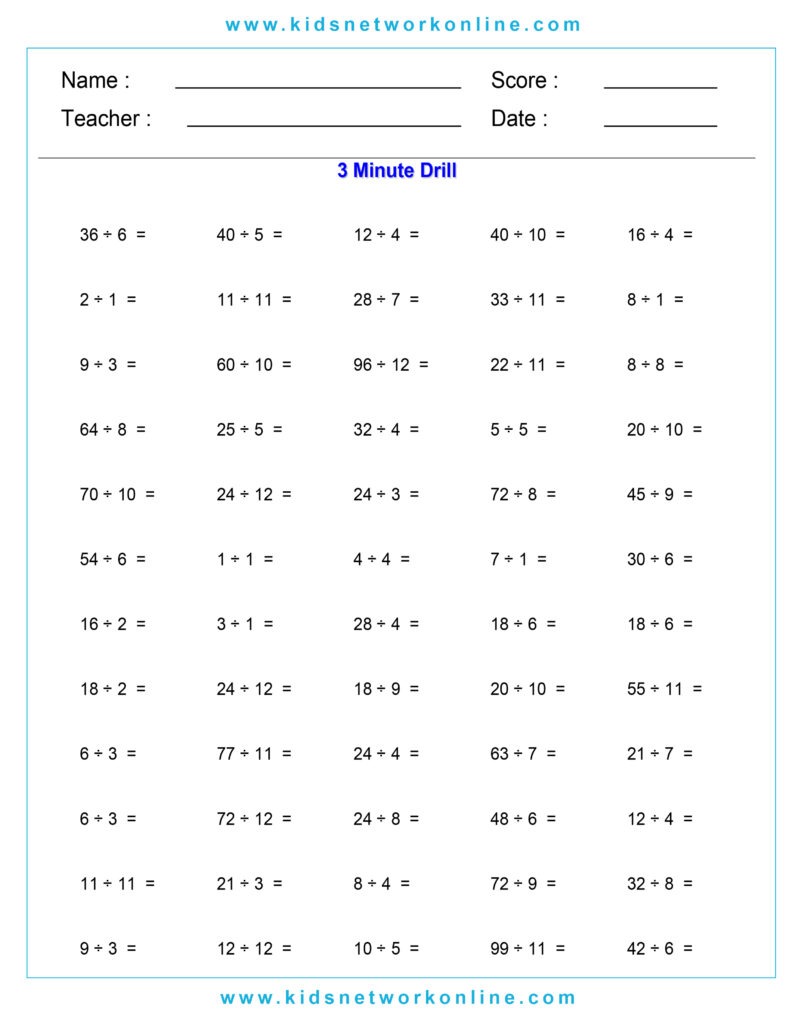
What is a division table?
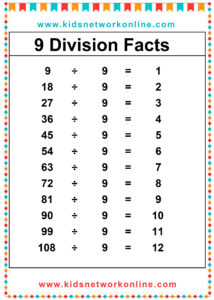
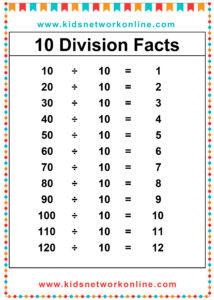
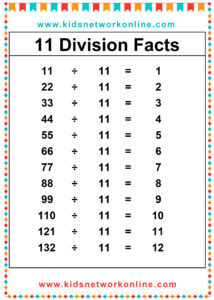
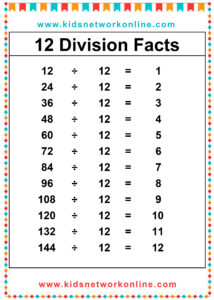
The division table is a chart that consists of lists of divisions. Usually, this table is used to help kids memorize and understand the process and the result of divisions. It commonly shows the divisions of numbers 0 to 10. However, we can also find lists of 0 to 12 divisions. Actually, the division table is a reversed form of the multiplication table.
How to Complete a Division Table
A division table organizes division facts, usually for divisors 1 through 10 or 12. It shows the quotient (result) for dividends divided by a specific divisor. To build one, choose a divisor. Then, use multiples of that divisor (like 0, n, 2n, up to 10n or 12n) as the dividends. Calculate the quotient for each dividend (Dividend ÷ Divisor). Repeat this process for each divisor from 1 up to the chosen limit.
What are the Division Formulas?
Division is the inverse operation of multiplication. It can be thought of as repeated subtraction. A division problem has three parts: the Dividend (the number being divided), the Divisor (the number you divide by), and the Quotient (the result). The main formula is: Dividend ÷ Divisor = Quotient.
Special cases include:
- Dividing by One: Any number divided by 1 is the number itself (e.g., 7 ÷ 1 = 7).
- Dividing by Zero: Division by zero is undefined.
- Dividing a Non-Zero Number by Itself: A non-zero number divided by itself is always 1 (e.g., 5 ÷ 5 = 1).
–Division Worksheets–
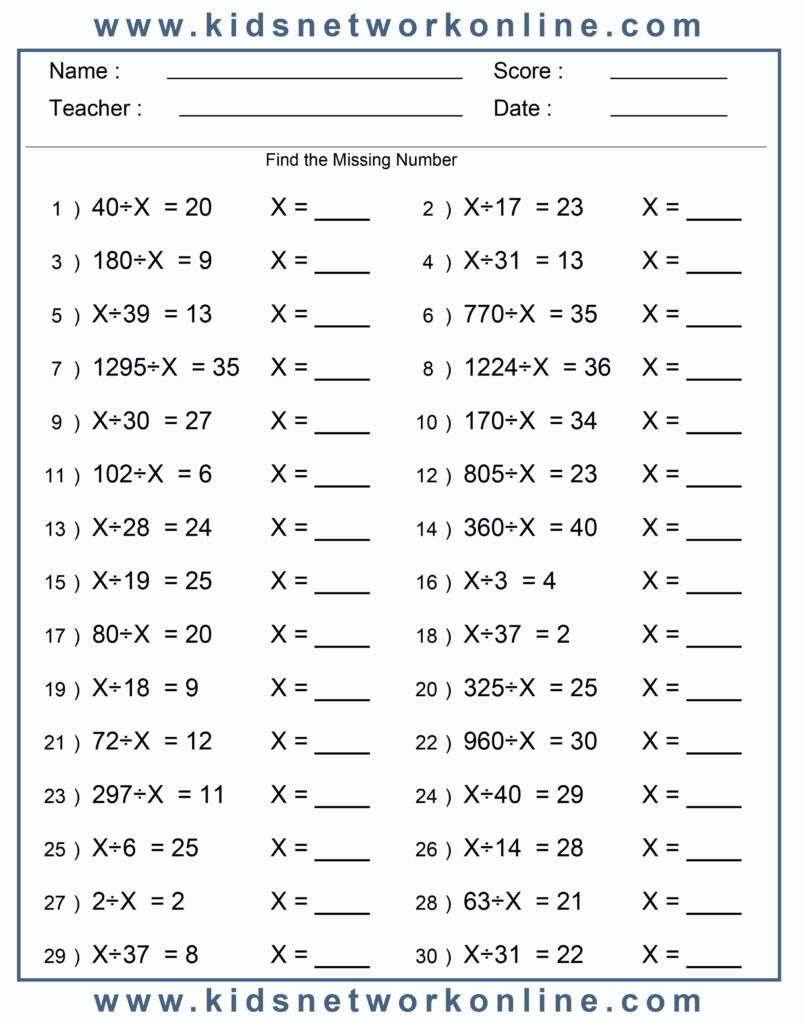
Division missing number worksheets –
help students practice division facts and problem-solving by finding the unknown value in a division equation.
These worksheets can be used to reinforce times tables, assess student understanding, and can be adapted for various learning levels.
Various Formats:Worksheets may include horizontal or vertical problem layouts, and some may use symbols like ÷ or /.
Missing Numbers:Students need to find the missing dividend, divisor, or quotient in division equations.
Inverse Operations:Finding the missing number often involves using the inverse operation of multiplication, or related multiplication facts.
Differentiation:Worksheets can be differentiated by difficulty, with options for different times tables or number ranges.
Engaging Activities:Some worksheets incorporate games or interactive elements to make learning fun and engaging.
Assessment:These worksheets can be used as a quick way to assess student progress and understanding of division.